Google Ads copywriting is an essential skill for online marketers and businesses. It involves creating compelling ad text that grabs attention and drives conversions. Well-crafted ad copy has the power to captivate your audience and drive them to take action.
Effective Google Ads copy follows certain rules and best practices. These include adhering to character limits, using relevant keywords, and creating clear calls-to-action. Marketers should focus on highlighting unique selling points and addressing customer pain points in their ads.
Experimenting with different versions of ad copy can help improve performance. This involves A/B testing various headlines, descriptions, and calls-to-action to find what resonates best with the target audience. By analyzing performance data, advertisers can make informed decisions to optimize their Google Ads campaigns.
Understanding Google Ads
Google Ads is a powerful online advertising platform. It helps businesses reach potential customers through targeted ads. The system uses keywords and user data to show relevant ads to people searching online or browsing websites.
The Fundamentals of Google Ads
Google Ads works on a pay-per-click model. Advertisers only pay when someone clicks on their ad. The platform uses an auction system to decide which ads to show.
Advertisers choose keywords related to their business. They create ads and set a budget. Google then displays these ads when people search for those keywords.
Ad Quality Score is important. It affects ad position and cost. Factors like relevance and landing page quality impact this score.
Targeting options include location, device, and time of day. This helps reach the right audience at the right time.
Elements of High-Converting Ad Copy
Great Google Ads copy grabs attention, engages readers, and builds trust. These key elements work together to boost click-through rates and conversions.
Headlines That Capture Attention
Compelling headlines are crucial for ad success. They should be clear, concise, and relevant to the search query. Use strong action words and numbers to stand out.
Include the main keyword in your headline. This helps match user intent and improves ad relevance.
Try asking questions or addressing pain points. For example: “Tired of Slow Internet?” or “Save 50% on Web Hosting”
Use power words like “exclusive,” “limited time,” or “guaranteed” to create urgency. But don’t overdo it or make false claims.
Test different headline formats:
- How-to: “How to Boost Your Website Traffic”
- Lists: “5 Ways to Improve SEO”
- Benefits: “Get More Leads with Google Ads”

Descriptions That Engage Readers
Ad descriptions expand on your headline and motivate action. Keep them clear and focused on benefits.
Highlight your unique selling points. What makes your offer better than competitors?
Use short sentences and simple language. Break up text with bullet points for easy scanning.
Include a clear call-to-action (CTA). Tell readers exactly what to do next: • “Shop Now” • “Get Your Free Quote” • “Sign Up Today”
Add credibility boosters like:
- Customer reviews
- Industry awards
- Performance stats
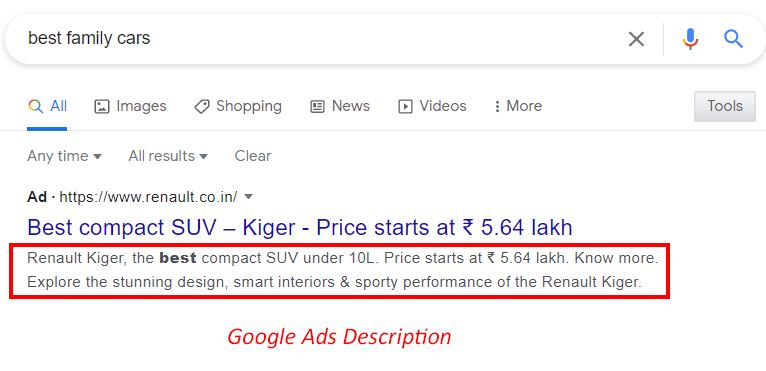
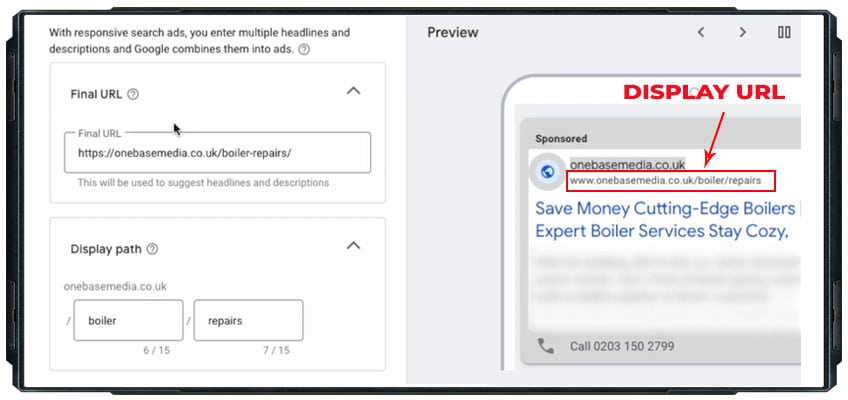
Display URLs That Enhance Credibility
Your display URL is the web address shown in your ad. It affects click-through rates and trust.
Use your main keyword in the display URL when possible. This reinforces relevance and can improve quality score.
Keep it short and memorable. Long, complex URLs can look spammy or untrustworthy.
Consider using subdomains or folders to add context. For example:
-
- “deals.yoursite.com”
Match your display URL to your landing page URL as closely as possible. This creates a smooth user experience and builds trust.
Writing Techniques for Google Ads
Effective Google Ads copy uses proven strategies to grab attention and drive conversions. These techniques help create compelling ads that resonate with target audiences and inspire action.
The AIDA Model
The AIDA model stands for Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. This framework guides Google Ads copywriting to engage users.
Attention: Use catchy headlines or questions to stop scrolling.
Interest: Highlight key benefits or unique selling points.
Desire: Create emotional connections or showcase solutions.
Action: Include clear calls-to-action (CTAs) to drive clicks.
Implement AIDA in ad headlines, descriptions, and extensions. Test different approaches to find what works best for each campaign.

Using Emotional Triggers
Emotions play a big role in decision-making. Tap into feelings to make ads more compelling.
Some powerful emotional triggers include:
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Desire for belonging
- Need for security
- Hope for a better future
Incorporate social proof like customer reviews or ratings. This builds trust and credibility.
Use words that evoke specific emotions related to your product or service. Match the emotional tone to your brand voice and target audience

Clarity and Brevity in Copy
Google Ads have limited space. Make every word count.
Use simple language at an 8th-grade reading level. Avoid jargon or complex terms.
Focus on one main message per ad. Highlight the most important benefit or feature.
Write short, punchy sentences. Break up text with line breaks for easy scanning.
Include numbers and specifics when possible. For example: “Save 50% Today” is stronger than “Big Savings”.
Use keywords that match search queries. This improves relevance and quality scores.
Test different versions of ad copy to find what performs best. Continuously refine based on data and results

Optimizing Ads for Performance
Google Ads copywriting goes beyond crafting compelling messages. It involves strategic optimization to boost ad performance and drive conversions. This process includes careful keyword selection, ad customization, and continuous testing.
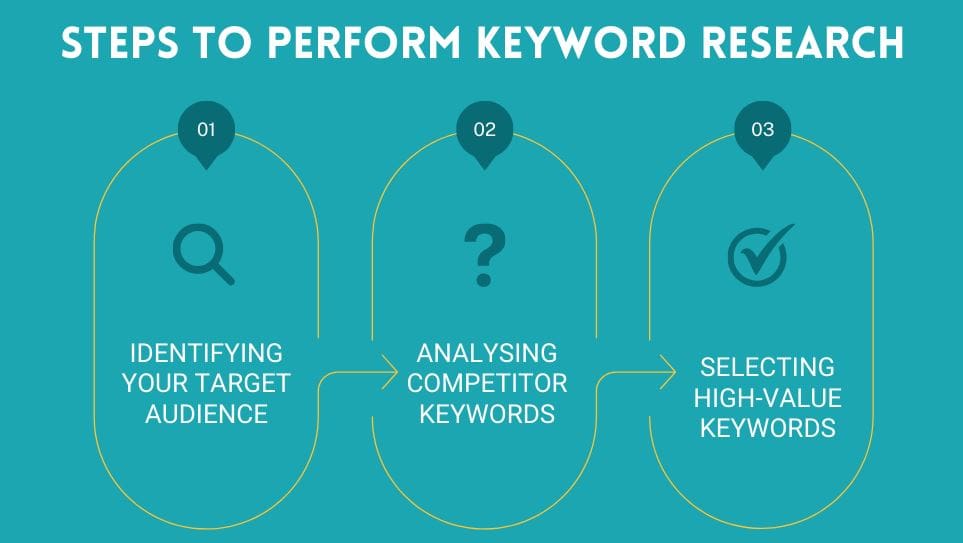
Keyword Research and Selection
Effective keyword research forms the backbone of successful Google Ads campaigns. Advertisers need to identify terms their target audience uses when searching for products or services.
Long-tail keywords often yield better results. They are more specific and tend to have lower competition. This can lead to higher click-through rates and conversions.
Using keyword match types wisely is crucial. Broad match can increase reach but may result in irrelevant clicks. Exact match ensures precision but limits visibility. Phrase match offers a balance between reach and relevance.
Negative keywords help prevent ads from showing for irrelevant searches. This improves ad relevance and saves budget for more promising opportunities.
Ad Customization and Personalization
Tailoring ad copy to specific audiences can significantly boost performance. Advertisers should segment their audience based on demographics, interests, or behavior.
Dynamic keyword insertion allows ads to automatically include the user’s search term. This increases relevance and can improve click-through rates.
Location-based customization can make ads more appealing to local audiences. Including city names or region-specific offers can increase engagement.
Ad extensions provide extra information and increase ad visibility. These can include site links, callouts, or structured snippets
Testing and Iterating
Continuous testing is key to improving ad performance. A/B testing different headlines, descriptions, and calls-to-action helps identify what resonates best with the audience.
Advertisers should monitor key metrics like click-through rate, conversion rate, and quality score. These indicators help gauge ad effectiveness and guide optimization efforts.
Regular review of search term reports can uncover new keyword opportunities or reveal the need for additional negative keywords.
Ad rotation settings should be carefully considered. Optimizing for clicks or conversions can help achieve specific campaign goals

Compliance and Best Practices
Google Ads has rules advertisers must follow. These rules help create good ads and landing pages. Following them leads to better results.
Ad Policies and Guidelines
Google has strict ad policies for Google Ads. Ads must be honest and clear. They can’t mislead people or make false claims. Ads also need to follow trademark rules.
Some products have extra rules. For example, ads for medicine or finance have special guidelines. It’s key to know these rules for your industry.
Google checks ads before they go live. They may reject ads that break rules. This can delay campaigns. To avoid this, study the policies before writing ads

Landing Page Optimization
The landing page is where people go after clicking an ad. It needs to match what the ad promises. If not, people may leave quickly.
Good landing pages load fast. They work well on phones and computers. The main message should be clear right away.
Include a strong call to action. This tells people what to do next. It could be “Buy Now” or “Sign Up.”
Make sure the page is easy to use. Don’t ask for too much info at once. Keep forms short and simple.
Test different versions of your landing page. This helps find what works best. Small changes can make a big difference in how many people take action








